VMware Network Principles
VMware is a virtualization platform that only provides Layer 2 network switching functionality and does not have complete network management capabilities. Cloudpods supplements network management capabilities for VMware, providing IP address and network configuration information management capabilities.
Basic Concepts
VMware has the following basic network concepts:
Standard Virtual Switch (Standard vSwitch)
Multiple virtual switches can be configured within each ESXi host to implement network switching between virtual machines and between virtual machines and external physical networks.
Distributed Virtual Switch (Distributed vSwitch)
Multiple hosts managed by vCenter can define shared distributed virtual switches to implement unified configuration Layer 2 network switching between virtual machines across ESXi hosts.
Port
Virtual network port where virtual machines connect to virtual switches.
Standard Port Group
A group of virtual ports on a standard virtual switch that share the same VLAN, security policies, redundancy and other configurations.
Distributed Port Group
A group of virtual ports on a distributed virtual switch.
Basic Principles
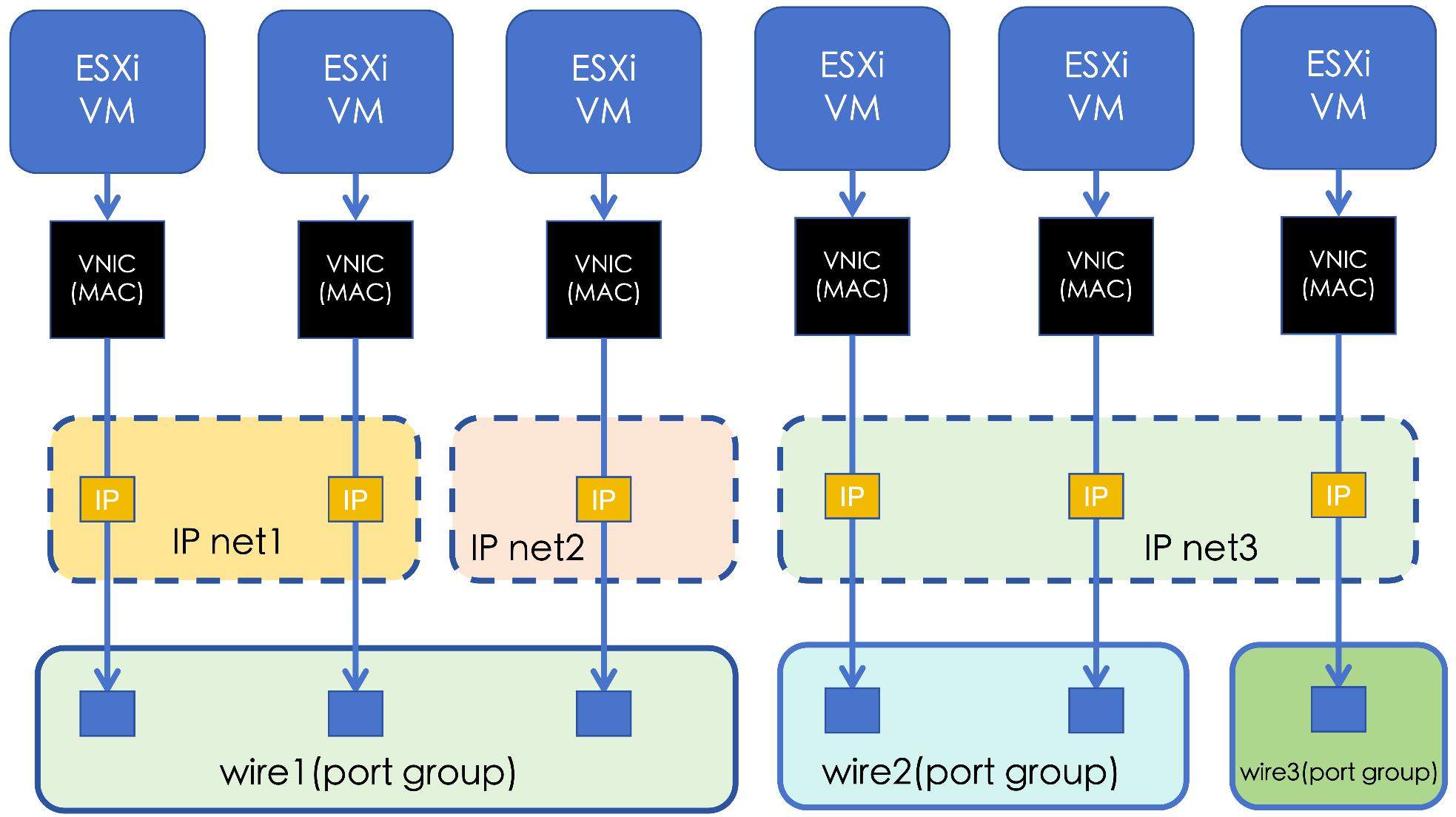
For version 3.10 and earlier, virtual switches in VMware correspond one-to-one with Layer 2 networks on the platform. IP subnets correspond to distributed port groups. IP subnets and distributed port groups are associated through VLAN IDs. This mapping method is relatively obscure and not easy to configure.
Starting from 3.11, port groups in VMware correspond one-to-one with Layer 2 networks on the platform. VMware is not responsible for maintaining IP subnet information. Therefore, IP subnet information that can be allocated on each port group is maintained in the platform.
The following summarizes the relationship between VMware-related concepts and platform-related concepts.
| VMware Concept | Platform Concept | How to Associate | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Machine | Virtual Machine | Associated through virtual machine UUID | One-to-one |
| ESXi Host | Host | Managed through host management IP | One-to-one |
| Port | Virtual NIC | Associated through IP address and MAC | One-to-one |
| Port Group | Layer 2 Network | Associated through port group ID | One-to-one |
| None | IP Subnet | NA | NA |
When managing a VMware cloud account, the platform will synchronize port group information and automatically create a one-to-one corresponding Layer 2 network for each port group. Because VMware is not responsible for virtual machine IP address management, IP subnet information on Layer 2 networks after synchronization needs to be maintained by administrators on the platform.
VMware IP Subnet Maintenance
Platform virtual machine virtual NICs contain the following four pieces of information: associated virtual machine, connected IP subnet, virtual NIC IP address and MAC address. Because VMware is not responsible for maintaining IP subnet information, after managing a VMware cloud account, we can only know the MAC address of each virtual machine's connected virtual NIC and the connected port group (and corresponding Layer 2 network). Furthermore, if matching version VMware Tools software is installed and running in the VMware virtual machine, the VMware platform can also obtain the IP address configured in the virtual machine through VMware tools. But due to missing IP subnet information, VMware virtual machines after initial management do not have virtual NIC records. For user convenience, if the virtual machine's IP address can be obtained through VMware Tools, this IP address information will be recorded in the virtual machine's tags, but this is only a marker. In order for managed VMware virtual machines to have virtual NIC records, appropriate IP subnets need to be created on the platform.
IP subnets need to be created on Layer 2 networks. IP subnets created on a VMware Layer 2 network should include IP addresses of virtual machines connected to the port group corresponding to this Layer 2 network. Therefore, for the convenience of maintaining IP subnets, it is recommended that an IP subnet's network segment only be used within one VMware port group.
After creating IP subnets, synchronize the VMware cloud account again. For VMware virtual machines whose IP addresses can be detected, the platform will find the corresponding IP subnet on the corresponding Layer 2 network based on their IP addresses and create corresponding virtual NIC records. For VMware virtual machines whose IP addresses cannot be detected, the platform cannot automatically create corresponding virtual NICs. At this time, users can manually specify the virtual machine's IP address through the fix IP address interface. The platform will find the IP subnet on the Layer 2 network corresponding to the virtual machine's port group based on this IP address, create a corresponding virtual NIC record, and occupy this IP address.
The platform defaults to supporting an IP subnet belonging to only one Layer 2 network, but in actual usage scenarios, there are cases where a continuous IP address segment is used by virtual machines scattered across multiple port groups. At this time, when creating an IP subnet, administrators need to first specify a default Layer 2 network. During creation, the platform will automatically detect whether this IP subnet is also used by other VMware Layer 2 networks (virtual machines on them). If it exists, it will automatically set the corresponding Layer 2 network as an additional Layer 2 network for this IP subnet. After creation, administrators can also manually set additional Layer 2 networks for this IP subnet. A virtual machine belonging to an additional Layer 2 network of an IP subnet can also use IPs from this IP subnet.
VMware New Host IP Address Allocation
When creating VMware virtual machines in the platform, the platform will automatically allocate an IP address to the virtual machine from the IP subnet connected to the virtual machine, and at the same time, based on the association relationship between the IP subnet and Layer 2 network (port group) and host, allocate the virtual machine to a host that can use this IP subnet. When creating this virtual machine on the VMware platform, the platform will find a port group corresponding to this IP subnet on the ESXi host in VMware (if there are multiple, select one) to allocate a port for the virtual machine, and associate the virtual machine's virtual NIC with this port group. During the deployment configuration phase, deploy the network configuration corresponding to this NIC in the virtual machine, including IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS and other configuration information. After the virtual machine starts, this virtual NIC is automatically configured and can be used immediately.
Common Operations
Fix VMware Virtual Machine IP Address
When VMware Tools in a VMware virtual machine is not working, the IP address cannot be obtained through the API. At this time, you need to manually set the virtual machine's IP address on the platform through the fix IP address interface.
climc server-sync-fix-nics <ID> <IP> ...
Specify Additional Layer 2 Networks for IP Subnet
If an IP subnet's IP addresses are used by virtual machines scattered across multiple Layer 2 networks, you need to set additional Layer 2 networks for this IP subnet to ensure that virtual machines connected to these Layer 2 networks can also allocate IPs from this IP subnet.
climc network-sync-additional-wires <NETID> --wire-ids <WIRE_ID> ...