Typical Network Configuration
This article introduces several typical private cloud network configurations
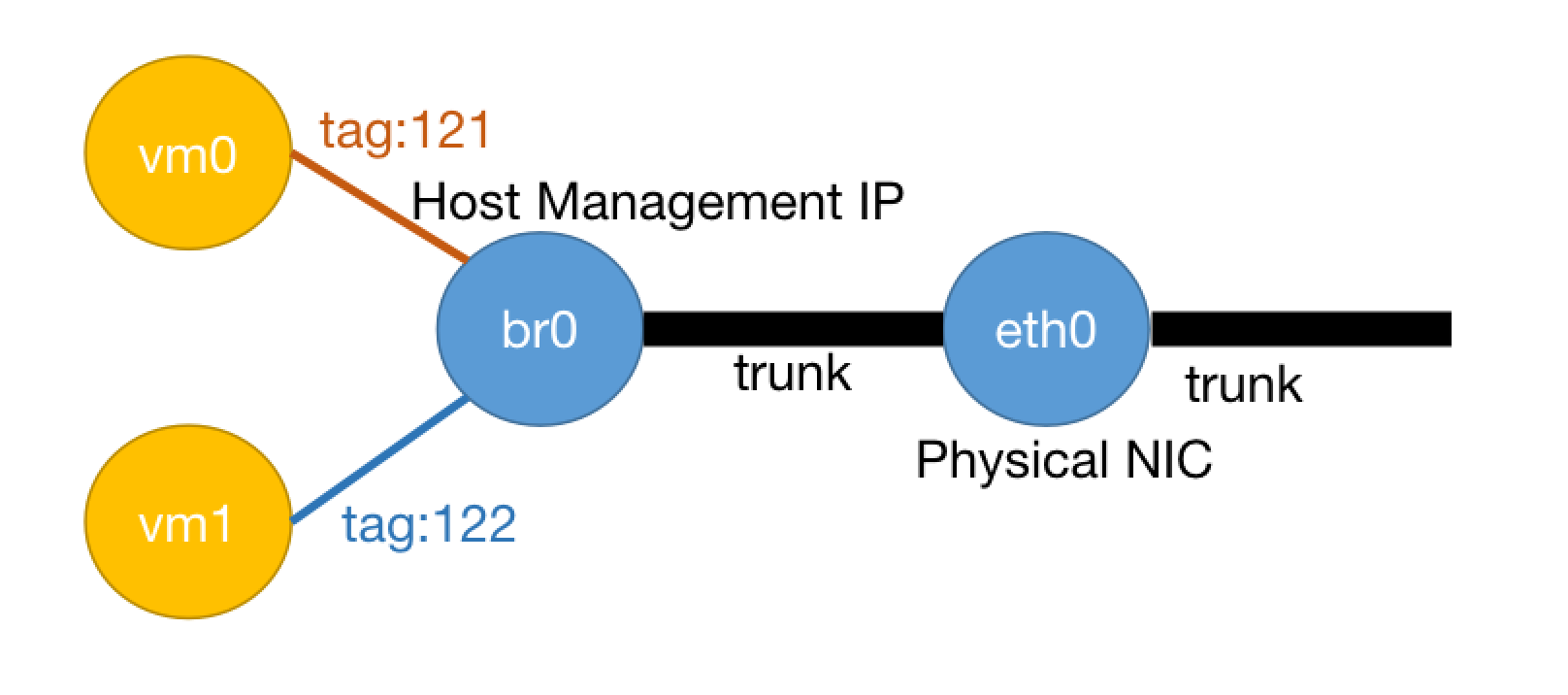
(Single Network Port Classic Network) Compute Node Single Network Port, Virtual Machines Use Multi-VLAN Classic Network
In this scenario, each compute node has only one network port (can be Bonding), serving as both management port and business port. Business traffic between virtual machines is forwarded by the layer 3 switch connected to the host.
VPC Configuration
Use Default VPC
Layer 2 Network Configuration
Create a layer 2 network bcast0 in Default VPC
IP Subnet Configuration
Create at least 2 IP subnets on layer 2 network bcast0. One IP subnet is for host management port use and needs to include the host's management port IP. Another subnet is for virtual machines. You can configure more IP subnets for virtual machines to use, and these virtual machine IP subnets can configure different VLAN IDs (VLAN IDs other than 1). Gateways and corresponding VLANs of these IP subnets need to be configured on the layer 3 switch connected to the physical machine.
Host Configuration
The host's network port needs to be configured as trunk mode on the switch. The host management port must use the default VLAN ID. Generally, the default VLAN ID is 1. However, currently switches also support setting non-1 VLAN IDs for TRUNK ports. For details, please refer to the switch configuration manual.
Host host.conf networks configuration:
networks:
- <host_ifname>/br0/<host_management_ip>
For example:
networks:
- eth0/br0/10.168.20.2
Host Management Port Uses Non-1 VLAN ID, and Switch Does Not Support Setting Default VLAN ID for TRUNK Ports. How to Configure in This Case?
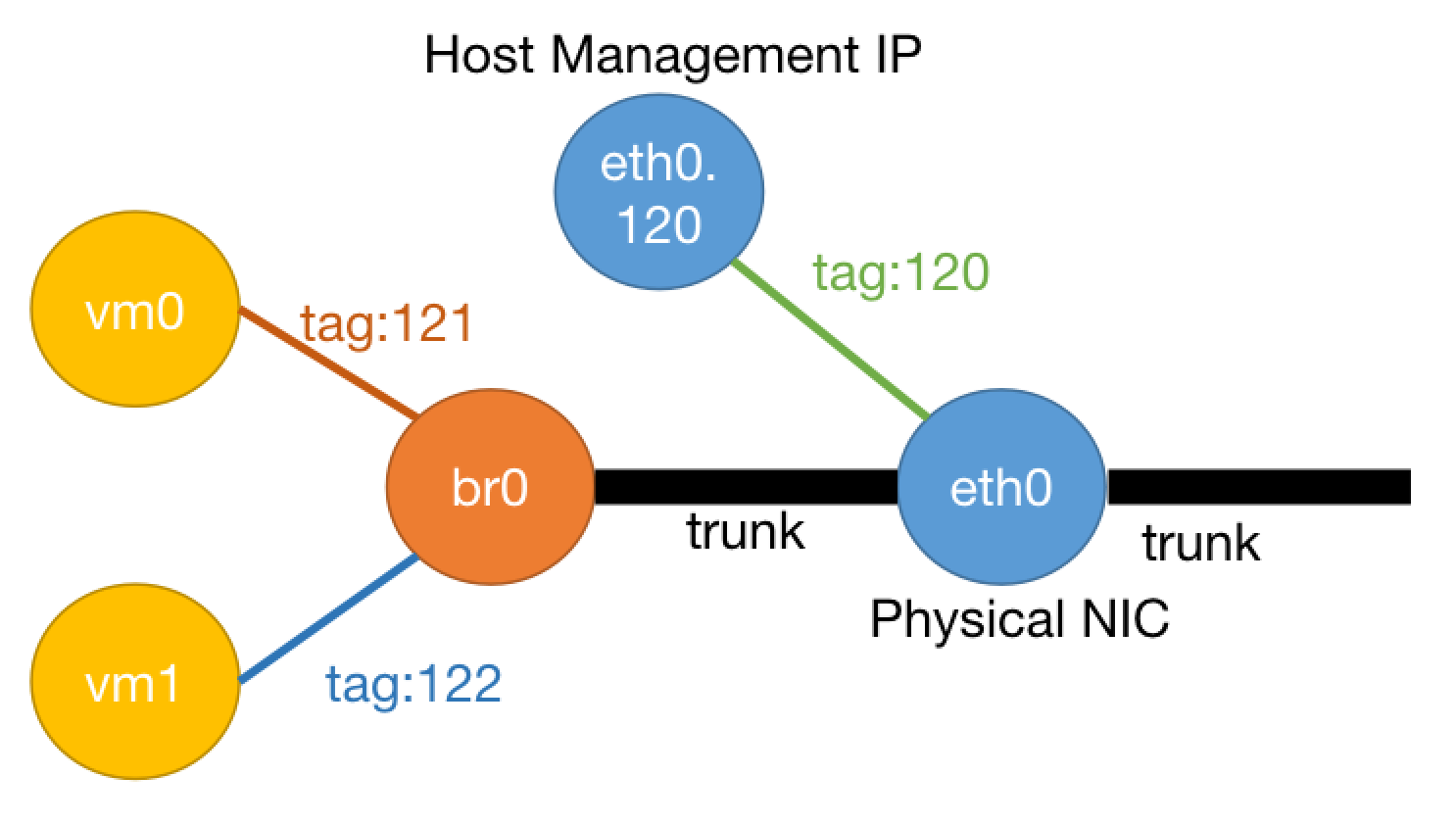
In this case, you need to set a VLAN sub-interface for the host. The host uses this VLAN sub-interface as the management port, and the virtual machine switch needs to bridge to the main interface. The following uses host main interface as bond0, host management port VLAN ID as 3001 as an example:
- Configure VLAN sub-interface bond0.3001 on the host, configuration is as follows:
# /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0.3001
VLAN=yes
NAME=bond0.3001
DEVICE=bond0.3001
IPADDR=<management_ip>
PREFIX=<prefix>
DEFROUTE=yes
ONBOOT=yes
- Modify /etc/yunion/host.conf, set as follows:
listen_interface: bond0.3001
networks:
- bond0/br0/bcast0
Note that under this configuration, virtual machines will not be able to use the same VLAN ID as the host (here 3001).
EIP Configuration
In classic network mode, external can directly access virtual machine IPs, no need to configure EIP
(Single Network Port VPC Network) Compute Node Single Network Port, Virtual Machines Use VPC Network
In this scenario, each compute node host has only one network port as the management port. The management port also carries business traffic, but business traffic between virtual machines goes through ovn's geneve tunnel encapsulation.
Host Network Configuration
The host's management port still connects to the classic network.
You need to configure layer 2 network bcast0 under Default VPC, and configure the IP subnet used by the host management port IP under this layer 2 network.
Host's host.conf networks configuration is the same as Single Network Port Classic Network mode
For example, host IP subnet is 10.128.26.2. Then the host's configuration is also:
networks:
- eth0/br0/10.128.26.2
Virtual Machine Network Configuration
Virtual machine networks are managed by VPC. Users can create any VPC and allocate any IP subnets within the VPC. IP subnets between different VPCs are isolated from each other and cannot access. IP subnets within the same VPC are not isolated from each other.
EIP Configuration
In this mode, you need to configure EIP for external access to virtual machines inside VPC from outside the cloud platform.
The simplest EIP configuration is to select a host, modify /etc/yunion/host.conf, set sdn_enable_eip_man to true. For more specific configuration methods, please refer to the documentation. The first host installed using ALL IN ONE mode automatically enables sdn_enable_eip_man.
EIP Gateway Routing Configuration
To use EIP, you also need to add an IP network segment for EIP allocation under platform bcast0 (note that EIP network segment should avoid being in the same network segment as the host's management IP, that is, the network address needs to be different. For example, if the host's management network port is 10.168.22.2/24, then the EIP network segment is 10.168.23.0/24), add a static route for the EIP network segment on the switch, set NextHop to the management port IP of the first host deployed in ALL IN ONE mode.
(Dual Network Card Classic Network) Compute Node Two Network Ports, Virtual Machines Use Multi-VLAN Classic Network
In this scenario, each compute node has two network ports, one as the management port and the other as the business port. Business traffic between virtual machines is forwarded by the layer 3 switch connected to the host's business port. However, some virtual machines need to connect to the management port.
VPC Configuration
Use Default VPC
Layer 2 Network Configuration
Create two layer 2 networks in Default VPC: bcast0 (management) and bcast1 (business)
IP Subnet Configuration
Create at least two IP subnets on bcast0. One IP subnet is for host management port use and needs to include the host's management port IP. Another subnet is for virtual machines that need to connect to the management network.
Create 1 or more IP subnets on bcast1 for virtual machines to use, and these virtual machine IP subnets can configure different VLAN IDs (VLAN IDs other than 1). Gateways and corresponding VLANs of these IP subnets need to be configured on the corresponding layer 3 switch connected to the physical machine.
Host Configuration
The host's management port needs to configure the management IP. This management port is in Access mode on the switch.
The host's business port does not need to configure an IP, but the business network port needs to be configured as trunk mode on the switch.
The host's /etc/yunion/host.conf needs to have two records, one for the management port and one for the business port
networks:
- <host_ifname0>/br0/<host_management_ip>
- <host_ifname1>/br1/bcast1
For example:
networks:
- eth0/br0/10.168.20.2
- eth1/br1/bcast1
EIP Configuration
In this mode, external can directly access virtual machine IPs, no need to configure EIP
(Dual Network Port VPC Network) Compute Node Two Network Ports, Virtual Machines Use VPC Network
In this scenario, each compute node host has two network ports. One is the management port, carrying management traffic. The other is the business port, carrying business traffic. Business traffic between virtual machines goes through ovn's geneve tunnel encapsulation and is forwarded through the host's business port.
Host Network Configuration
Similarly, the host's management port uses classic network.
You need to configure layer 2 network bcast0 under Default VPC, and configure the IP subnet used by the host management port under this layer 2 network.
For example, host IP subnet is 10.128.26.2. Then the host's /etc/yunion/host.conf configuration is:
networks:
- eth0/br0/10.128.26.2
At the same time, the host's business port also needs to configure an IP, and this business port IP and management port IP should not be in the same layer 2 network.
To ensure ovn traffic between virtual machines goes through the business port, you need to configure /etc/yunion/host.conf's ovn_encap_ip as the host's business port IP.
For example, the host's management port IP is 10.128.26.2/24, business port IP is 10.129.26.2/24, then /etc/yunion/host.conf configuration is:
ovn_encap_ip: 10.129.26.2
networks:
- eth0/br0/10.128.26.2
- eth1/br1/10.129.26.2
After configuration, VPC network traffic between virtual machines will all be encapsulated as geneve traffic with source and destination IP addresses in the business network segment. The network only needs to ensure network connectivity between business ports. Whether the host's business port VLAN mode is TRUNK or Access does not affect it.
Virtual Machine Network Configuration
Similarly, in this mode, virtual machine networks are managed by VPC. Users can create any VPC and allocate any IP subnets within the VPC. IP subnets between different VPCs are isolated from each other and cannot access. IP subnets within the same VPC are not isolated from each other. Since the host has configured ovn_encap_ip as the host's business port IP, ovn traffic between virtual machines is all forwarded through the host's business port.
EIP Configuration
In VPC network mode, you need to configure EIP for external access to specified internal virtual machines. Similarly, you also need to configure EIP gateway and EIP network segment.
EIP Gateway Routing Configuration
The difference from Single Network Port VPC Network is that to ensure EIP traffic also goes through the business port, you need to ensure the following two configurations:
- When configuring the NextHop for the EIP network segment on the switch, you need to use the business network port IP of the node where the EIP gateway is located as the NextHop IP. (Ensure EIP incoming traffic goes through the business port)
- On the node where the EIP gateway is located, you need to set the business port as the default route exit. (Ensure EIP outgoing traffic goes through the business port)