VPC NAT
This article introduces VPC network's NAT functionality.
VPC networks are isolated virtual networks. Users can configure any IP network segments within VPC networks as needed. VPC networks implement interconnection of IP subnets within the same VPC.
VPC's external network access mode is determined by ExternalAccessMode. Possible values are
| ExternalAccessMode | Description |
|---|---|
| eip | Access external network through EIP, only virtual machines with EIP mounted can access |
| distgw | Access external network through host's distributed NAT gateway |
| eip-distgw | If virtual machine does not have EIP mounted, access external network through distributed NAT gateway, otherwise access external network through EIP. This is the default method |
| none | Virtual machines cannot access external network through VPC |
When VPC enables distributed NAT gateway functionality, virtual machines in VPC need to access external gateways through NAT gateway to access external networks.
As shown in the figure below, when VM accesses external networks, its traffic is forwarded by VPC to NAT gateway. NAT gateway then forwards packets sent by VM to the destination address, and at the same time converts the IP packet's source address to NAT gateway's physical network IP address.
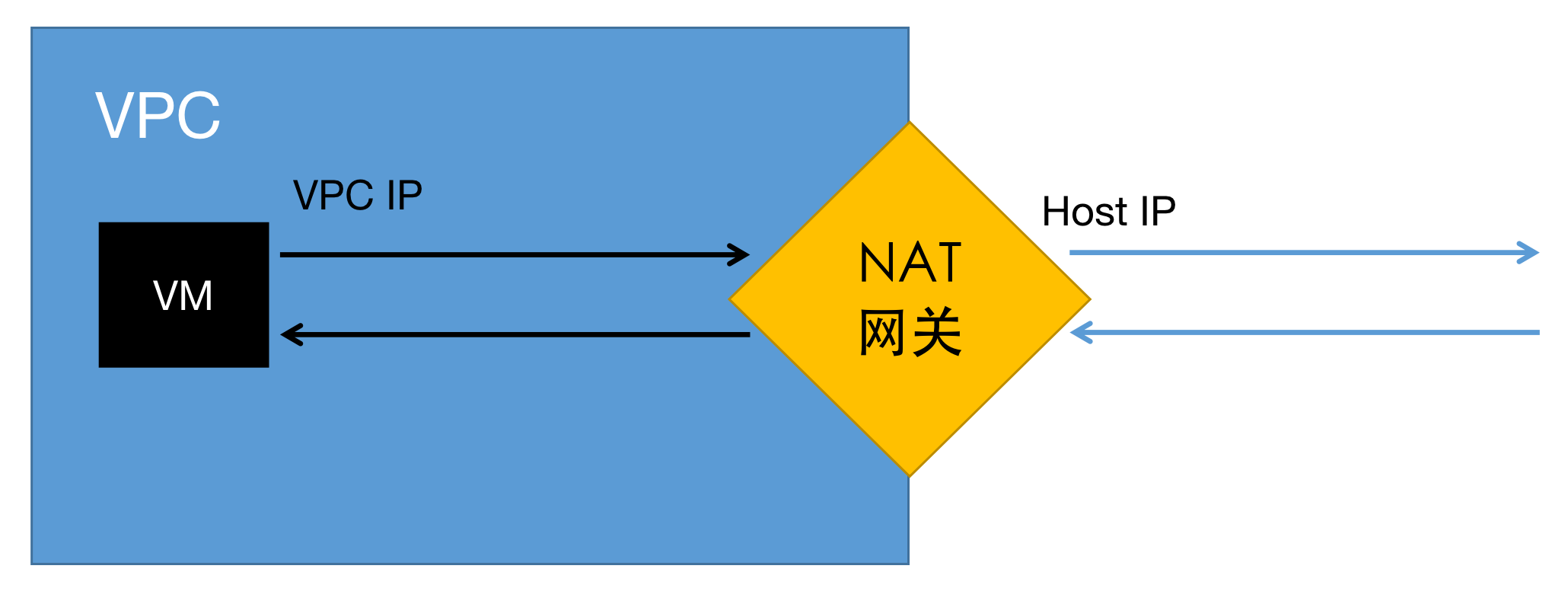
The platform implements distributed NAT functionality, that is, each host is a NAT gateway, responsible for forwarding traffic of VPC virtual machines on this host accessing external networks. Therefore, as long as the host can access external networks, virtual machines in VPC can access external networks.
Modify VPC External Network Access Mode
You can modify VPC's external network access mode through climc commands, for example
climc vpc-update --external-access-mode eip vpc0