Backend Service Framework
Introduction to the framework and related libraries used by cloud platform backend services. It is recommended to first read Development Guide/Service Component Introduction to understand the general functions of each service.
Backend Service Framework
Backend services such as keystone, region, and glance all use the same backend service framework, which we defined and implemented ourselves. The core modules are as follows:
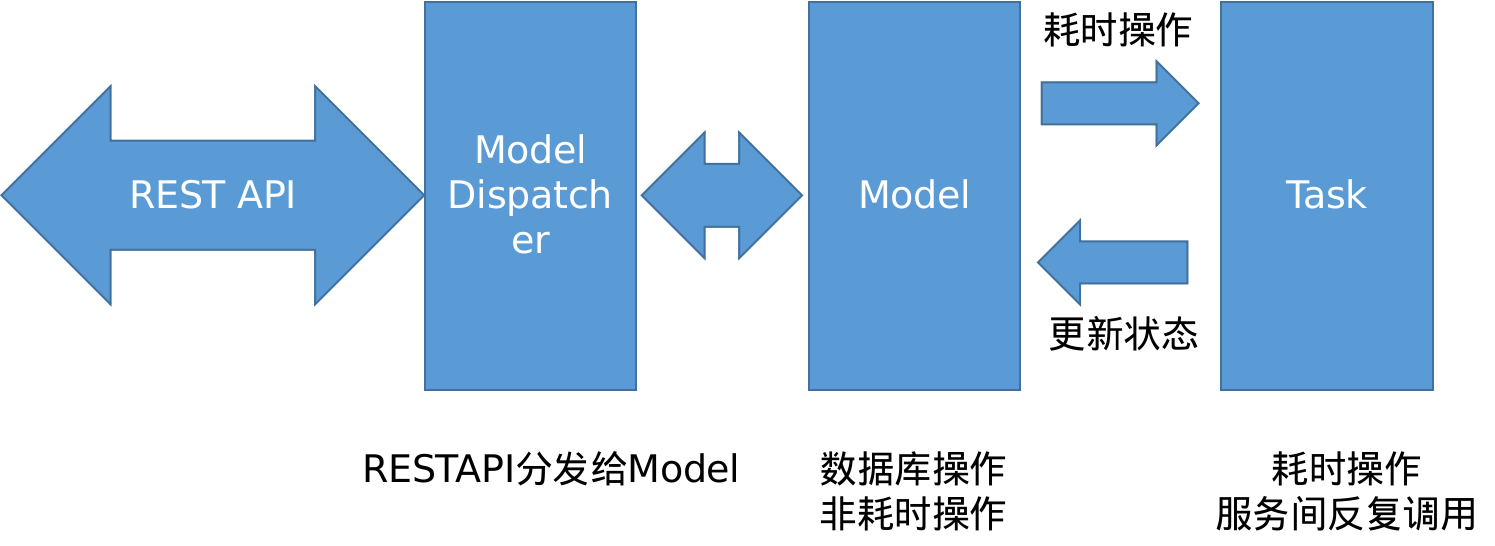
-
REST API: Responsible for parsing CRUD http requests sent by clients and mapping different requests to the Model Dispatcher module.
-
Model Dispatcher: Distributes client requests to business operations of corresponding resources.
-
Model: Defines various resources of the cloud platform, performs database read and write operations. If specific business needs time-consuming operations, they will be executed through the Task mechanism.
-
Task: Module for background processing of asynchronous time-consuming tasks, updates task execution results by updating Model status.
Cloudpods Code Structure
- build: RPM packaging scripts
- cmd: Executable binary entry programs
- pkg: Libraries
- appsrv: Common http service framework
- cloudcommon: Cloud platform service framework, extended based on appsrv
- cloudcommon/options: Common options
- cloudcommon/app: Common service initialization code
- cloudcommon/db: Basic implementation of Model dispatcher and Models
- cloudcommon/db/lockman: Lock implementation
- cloudcommon/db/taskman: Asynchronous task framework
Authentication Part
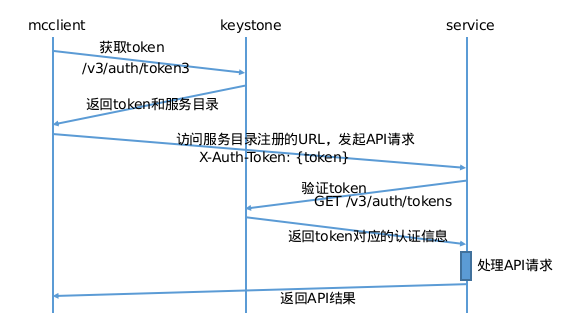
- Before clients send requests to services, they need to obtain a token from keystone
- Clients obtain tokens by calling keystone's /v3/auth/tokens interface with username and password
- Each API request sent by clients to services will carry this token in the HTTP header, for example: X-Auth-Token: {token}
- Backend services verify this token with keystone, obtain user identity information, and execute subsequent API processes
- Each service has a keystone-registered service user account (user/password) and joins the system project with admin role
- After service startup, it will authenticate with keystone to obtain an admin token
- When users access services through API, they will carry a token in the header
- Use this admin token to access keystone's token verification interface, verify this token, and obtain user identity information
Model Dispatcher
Maps REST API and Manager/Model methods one-to-one
| REST API Request | API Function | Corresponding Object | Framework Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET /$resources | List | Manager | ListItemFilter | Filter |
| - | Manager | FetchCustomizeColumns | Get extended field information | |
| GET /<resources>/<property> | Get this type of resource specific property | Manager | GetProperty<Property> | Get this type of resource specific property |
| GET /<resources>/<res_id> | Get a resource details | Model | FetchCustomizeColumns | Get extended field information |
| GET /<resources>/<res_id>/<spec> | Get a resource specific property | Model | GetDetails<Spec> | Get a resource specific property |
| POST /<resources> | Create resource | Manager | ValidateCreateData | Validate and process creation data |
| - | Model | CustomizeCreate | Custom creation operation | |
| - | Model | PostCreate | Hook after creation | |
| - | Manager | OnCreateComplete | Hook after creation completion | |
| POST /<resources>/<action> | Execute operation on this type of resource | Manager | Perform<Action> | Execute specific operation on this type of resource |
| POST /<resources>/<res_id>/<action> | Execute operation on a resource | Model | Perform<Action> | Execute specific operation on a resource |
| PUT /<resources>/<res_id> | Update a resource properties | Model | ValidateUpdateData | Validate and process update operation data |
| - | Model | PreUpdate | Custom creation operation | |
| - | Model | PostUpdate | Hook after creation | |
| DELETE /<resources>/<res_id> | Delete a resource | Model | CustomizeDelete | Custom delete operation |
| - | Model | PreDelete | Hook before deletion | |
| - | Model | Delete | Execute delete operation | |
| - | Model | PostDelete | Hook after deletion |
The binding function for specific restful requests is in: pkg/appsrv/dispatcher/dispatcher.go file's AddModelDispatcher function.
Database ORM Model
Code located at cloudcommon/db
- Interfaces
- IModelManager: Corresponds to the table of resources in the database
- IModel: Corresponds to a single piece of data of resources in the database
- Data Structures
- SResourceBase: Base resource
- SStandaloneResourceBase: Physical resources of infrastructure, resources without specific ownerId, such as zone, host
- SVirtualResourceBase: Virtual resources, such as virtual machines (guest)
- SSharableVirtualResourceBase: Virtual shareable virtual resources, such as disk, network
- SAdminSharableVirtualInfoBase: Shareable virtual resources for management configuration, such as security group
- SSharableVirtualResourceBase: Virtual shareable virtual resources, such as disk, network
- SVirtualResourceBase: Virtual resources, such as virtual machines (guest)
- SJointResourceBase: Joint data type, such as virtual network card is the joint of virtual machine and network, virtual disk mount: joint of virtual machine and virtual disk
- SStandaloneResourceBase: Physical resources of infrastructure, resources without specific ownerId, such as zone, host
- SResourceBase: Base resource
Example
Using the virtual machine's model as an example, code is at: pkg/compute/models/guests.go.
GuestManager corresponds to guests_tbl in the database. This object nests db.SVirtualResourceBaseManager to indicate it's a Manager of virtual resources. This will default implement the db.IModelManager interface, and then it's convenient to override some methods according to business needs.
SGuest corresponds to each row of data in the guests_tbl database, managed by GuestManager, nested with db.SVirtualResourceBase structure. By default, it will have the table structure required for virtual resources, and then define some properties unique to virtual machines, such as VcpuCount representing cpu cores, VmemSize representing memory size. After code abstraction, it represents a virtual machine instance. This object will bind specific business operation implementation functions for virtual machines.
import "yunion.io/x/cloudpods/pkg/cloudcommon/db"
......
type SGuestManager struct {
db.SVirtualResourceBaseManager
}
var GuestManager *SGuestManager
func init() {
GuestManager = &SGuestManager{
SVirtualResourceBaseManager: db.NewVirtualResourceBaseManager(
SGuest{},
"guests_tbl",
"server",
"servers",
),
}
GuestManager.SetVirtualObject(GuestManager)
GuestManager.SetAlias("guest", "guests")
}
type SGuest struct {
db.SVirtualResourceBase
db.SExternalizedResourceBase
SBillingResourceBase
VcpuCount int `nullable:"false" default:"1" list:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(TINYINT, nullable=False, default=1)
VmemSize int `nullable:"false" list:"user" create:"required"` // Column(Integer, nullable=False)
BootOrder string `width:"8" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" default:"cdn" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(8, charset='ascii'), nullable=True, default='cdn')
DisableDelete tristate.TriState `nullable:"false" default:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(Boolean, nullable=False, default=True)
ShutdownBehavior string `width:"16" charset:"ascii" default:"stop" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(16, charset='ascii'), default=SHUTDOWN_STOP)
KeypairId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
HostId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"admin" get:"admin" index:"true"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
BackupHostId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" get:"user"`
Vga string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
Vdi string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
Machine string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
Bios string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
OsType string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" update:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
FlavorId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
SecgrpId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" get:"user" create:"optional"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
AdminSecgrpId string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" get:"admin"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
Hypervisor string `width:"16" charset:"ascii" nullable:"false" default:"kvm" list:"user" create:"required"` // Column(VARCHAR(16, charset='ascii'), nullable=False, default=HYPERVISOR_DEFAULT)
InstanceType string `width:"64" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true" list:"user" create:"optional"`
}
......
Database Locks
Code located at cloudcommon/db/lockman:
- LockClass/ReleaseClass: Lock a class of instances, generally needed when creating resources
- LockObject/ReleaseObject: Lock an instance, generally needed when modifying resource instances
- LockRawObject/RelaseRawObject: General lock
Example
The DoCreate function in pkg/cloudcommon/db/db_dispatcher.go will create the corresponding Model object and insert data into the database. At this time, locking is needed.
func DoCreate(manager IModelManager, ctx context.Context, userCred mcclient.TokenCredential, query jsonutils.JSONObject, data jsonutils.JSONObject, ownerId mcclient.IIdentityProvider) (IModel, error) {
lockman.LockClass(ctx, manager, GetLockClassKey(manager, ownerId))
defer lockman.ReleaseClass(ctx, manager, GetLockClassKey(manager, ownerId))
return doCreateItem(manager, ctx, userCred, ownerId, nil, data)
}
Worker Queue Management
To avoid unexpected concurrency, all asynchronously executed code should be executed within workers to facilitate concurrency management.
Code located at appsrv/workers.go
workerman := appsrv.NewWorkerManager(name, parallel_cnt, …)
workerman.Run(func() {…}, nil, nil)
Task Mechanism
Asynchronous time-consuming tasks of the cloud platform will be executed in the Task mechanism. For example, for virtual machine creation operations, after users submit requests, the region controller validates parameters and records data to the database, then immediately returns the corresponding virtual machine record to the client. At the same time, it will start executing the task of creating a virtual machine. This task will immediately execute in the background and will indicate execution success or failure by updating the virtual machine SGuest model status and recording operation logs.
Tasks are also records stored in the tasks_tbl database. The corresponding definition is in: pkg/cloudcommon/db/taskman/tasks.go. The data structure is as follows:
type STaskManager struct {
db.SResourceBaseManager
}
var TaskManager *STaskManager
func init() {
TaskManager = &STaskManager{
SResourceBaseManager: db.NewResourceBaseManager(STask{}, "tasks_tbl", "task", "tasks")
}
TaskManager.SetVirtualObject(TaskManager)
}
type STask struct {
db.SResourceBase
Id string `width:"36" charset:"ascii" primary:"true" list:"user"` // Column(VARCHAR(36, charset='ascii'), primary_key=True, default=get_uuid)
ObjName string `width:"128" charset:"utf8" nullable:"false" list:"user"` // Column(VARCHAR(128, charset='utf8'), nullable=False)
ObjId string `width:"128" charset:"ascii" nullable:"false" list:"user" index:"true"` // Column(VARCHAR(ID_LENGTH, charset='ascii'), nullable=False)
TaskName string `width:"64" charset:"ascii" nullable:"false" list:"user"` // Column(VARCHAR(64, charset='ascii'), nullable=False)
UserCred mcclient.TokenCredential `width:"1024" charset:"utf8" nullable:"false" get:"user"` // Column(VARCHAR(1024, charset='ascii'), nullable=False)
OwnerCred string `width:"512" charset:"ascii" nullable:"true"` // Column(VARCHAR (512, charset='ascii'), nullable=True)
Params *jsonutils.JSONDict `charset:"utf8" length:"medium" nullable:"false" get:"user"` // Column(MEDIUMTEXT(charset='ascii'), nullable=False)
Stage string `width:"64" charset:"ascii" nullable:"false" default:"on_init" list:"user"` // Column(VARCHAR(64, charset='ascii'), nullable=False, default='on_init')
taskObject db.IStandaloneModel `ignore:"true"`
taskObjects []db.IStandaloneModel `ignore:"true"`
}
- Id: The Id in STask is the Id of this task record
- ObjId: Corresponds to the Id of the resource object, used to record the resource of the corresponding operation executed by this task, such as the Id of a virtual machine or disk
- UserCred: Stores user information executing the task
- Params: Parameters for executing the task
- TaskName: Corresponds to the name of the task
- Stage: Stage of task execution, default is OnInit
Example
Using virtual machine shutdown as an example:
- After the client initiates a POST /servers/<server_id>/stop request, the service framework will execute the
func (self *SGuest) PerformStopfunction. Code snippet is as follows (located at: pkg/compute/models/guest_actions.go):
func (self *SGuest) PerformStop(ctx context.Context, userCred mcclient.TokenCredential, query jsonutils.JSONObject,
data jsonutils.JSONObject) (jsonutils.JSONObject, error) {
// XXX if is force, force stop guest
var isForce = jsonutils.QueryBoolean(data, "is_force", false)
if isForce || utils.IsInStringArray(self.Status, []string{api.VM_RUNNING, api.VM_STOP_FAILED}) {
return nil, self.StartGuestStopTask(ctx, userCred, isForce, "")
} else {
return nil, httperrors.NewInvalidStatusError("Cannot stop server in status %s", self.Status)
}
}
- SGuest will execute the self.StartGuestStopTask function, which will call different Drivers of the virtual machine to execute shutdown operations
// pkg/compute/models/guest_actions.go
func (self *SGuest) StartGuestStopTask(ctx context.Context, userCred mcclient.TokenCredential, isForce bool, parentTaskId string) error {
......
return self.GetDriver().StartGuestStopTask(self, ctx, userCred, params, parentTaskId)
}
// pkg/compute/guestdrivers/virtualization.go
import "yunion.io/x/cloudpods/pkg/cloudcommon/db/taskman"
......
func (self *SVirtualizedGuestDriver) StartGuestStopTask(guest *models.SGuest, ctx context.Context, userCred mcclient.TokenCredential, params *jsonutils.JSONDict, parentTaskId string) error {
task, err := taskman.TaskManager.NewTask(ctx, "GuestStopTask", guest, userCred, params, parentTaskId, "", nil)
if err != nil {
return err
}
task.ScheduleRun(nil)
return nil
}
......
-
taskman.TaskManager.NewTask(ctx, "GuestStopTask", ...) The GuestStopTask here corresponds to GuestStopTask in pkg/compute/tasks/guest_stop_task.go, which is found through a map maintained in taskman.
-
task.ScheduleRun(nil) will start executing the corresponding Task. By default, it will start executing from the task's default Stage OnInit function, so through the task mechanism it will execute to the GuestStopTask.OnInit function. The OnInit function will eventually call the corresponding virtual machine's driver to execute the RequestStopOnHost function and update its own Stage to OnMasterStopTaskComplete.
-
For virtual machines, the RequestStopOnHost function will request the host agent where the virtual machine is located to shut down the virtual machine. After successful shutdown, it will callback the region task framework. This framework will load GuestStopTask back from the database based on taskId, then execute according to the Stage OnMasterStopTaskComplete it set.
Here, failure will automatically call the OnGuestStopTaskCompleteFailed function, so when writing corresponding task stage functions, if you write <OnSometingComplete> functions, you must also write <OnSometingCompleteFailed> functions to handle failure cases.
- If shutdown is successful, OnMasterStopTaskComplete calls the OnGuestStopTaskComplete function, which will set the virtual machine's status to ready and record a shutdown operation log. If it fails, it will call the OnGuestStopTaskCompleteFailed function, which will set the virtual machine status to shutdown failed and record the reason for failure.
func (self *GuestStopTask) OnInit(ctx context.Context, obj db.IStandaloneModel, data jsonutils.JSONObject) {
guest := obj.(*models.SGuest)
db.OpsLog.LogEvent(guest, db.ACT_STOPPING, nil, self.UserCred)
self.stopGuest(ctx, guest)
}
func (self *GuestStopTask) stopGuest(ctx context.Context, guest *models.SGuest) {
host := guest.GetHost()
if host == nil {
self.OnGuestStopTaskCompleteFailed(ctx, guest, jsonutils.NewString("no associated host"))
return
}
if !self.IsSubtask() {
guest.SetStatus(self.UserCred, api.VM_STOPPING, "")
}
self.SetStage("OnMasterStopTaskComplete", nil)
err := guest.GetDriver().RequestStopOnHost(ctx, guest, host, self)
......
}
func (self *GuestStopTask) OnMasterStopTaskComplete(ctx context.Context, guest *models.SGuest, data jsonutils.JSONObject) {
......
self.OnGuestStopTaskComplete(ctx, guest, data)
}
func (self *GuestStopTask) OnMasterStopTaskCompleteFailed(ctx context.Context, obj db.IStandaloneModel, reason jsonutils.JSONObject) {
guest := obj.(*models.SGuest)
self.OnGuestStopTaskCompleteFailed(ctx, guest, reason)
}
func (self *GuestStopTask) OnGuestStopTaskComplete(ctx context.Context, guest *models.SGuest, data jsonutils.JSONObject) {
......
guest.SetStatus(self.UserCred, api.VM_READY, "")
......
logclient.AddActionLogWithStartable(self, guest, logclient.ACT_VM_STOP, "", self.UserCred, true)
}
func (self *GuestStopTask) OnGuestStopTaskCompleteFailed(ctx context.Context, guest *models.SGuest, reason jsonutils.JSONObject) {
......
db.OpsLog.LogEvent(guest, db.ACT_STOP_FAIL, reason.String(), self.UserCred)
self.SetStageFailed(ctx, reason.String())
logclient.AddActionLogWithStartable(self, guest, logclient.ACT_VM_STOP, reason.String(), self.UserCred, false)
}
How to Add a New Service
- Register a service-enabled account in keystone
- Register service and endpoint in keystone
- Refer to cloudpods/pkg/logger to implement service code
- Prepare a configuration file for the service, containing the following basic information
Assuming the service name is svc, user and password are svcuser, svcuserpassword, service listening address is: http://localhost:8866, region is LocalTest, the corresponding operations are as follows:
# Create service
$ climc service-create --enabled svc svc
# Create endpoint, corresponding service is svc
$ climc endpoint-create svc LocalTest internal http://localhost:8866
# Create user
$ climc user-create --password svcuserpassword --enabled svcuser
# Add user to system project
$ climc project-add-user system svcuser admin
Configuration information is as follows
region: LocalTest
port: 8866
auth_url: https://<keystone_url>:35357/v3
admin_user: svcuser
admin_password: svcuserpassword
admin_tenant_name: system